CASE STUDY
Eliminating Data Silos saves Healthcare Payer nearly $4 MM yearly
KEY OUTCOME
Explore how Data Ideology helped a healthcare organization eliminate data silos and save $4 MM yearly with an updated system.
How did Data Ideology solve this organization’s challenges?
CHALLENGE SUMMARY
Care managers at a healthcare payer organization are suffering from siloed data effecting data quality and hampering capabilities to make real time decisions creating risk for both members and the organization.
SOLUTION SUMMARY
Unify all data sources to eliminate data silos and redundancies giving personnel access to quality data that will improve care management capabilities.
GOING DEEPER ON THEIR CHALLENGE
Clinical personnel at a top regional health insurance organization were unable to make real time decisions about care management because of disparate data systems and data silos. Access to this data in real time would allow care managers to drive greater quality care for members. Some major hurdles attributed to these data silos included:
- Multiple manual processes to consolidate data
- Technical debt from duplicative data in multiple silos
- Decreased capacity to work on advanced analytics caused by the increased need for data wrangling
- The difficulties of building technical teams outside of IT
UNDERSTANDING DATA IDEOLOGY’S SOLUTION
Integrate disparate data sources from data silos into a quality data models (QDM) to help improve data integrity and standardization with the support of a holistic methodology that combines People (data experts), Process (data governance), and Technology (modern data platform). This proven framework will eliminate data fragmentation as well as enhance data exchange capabilities for the organization.
THE RESULTS
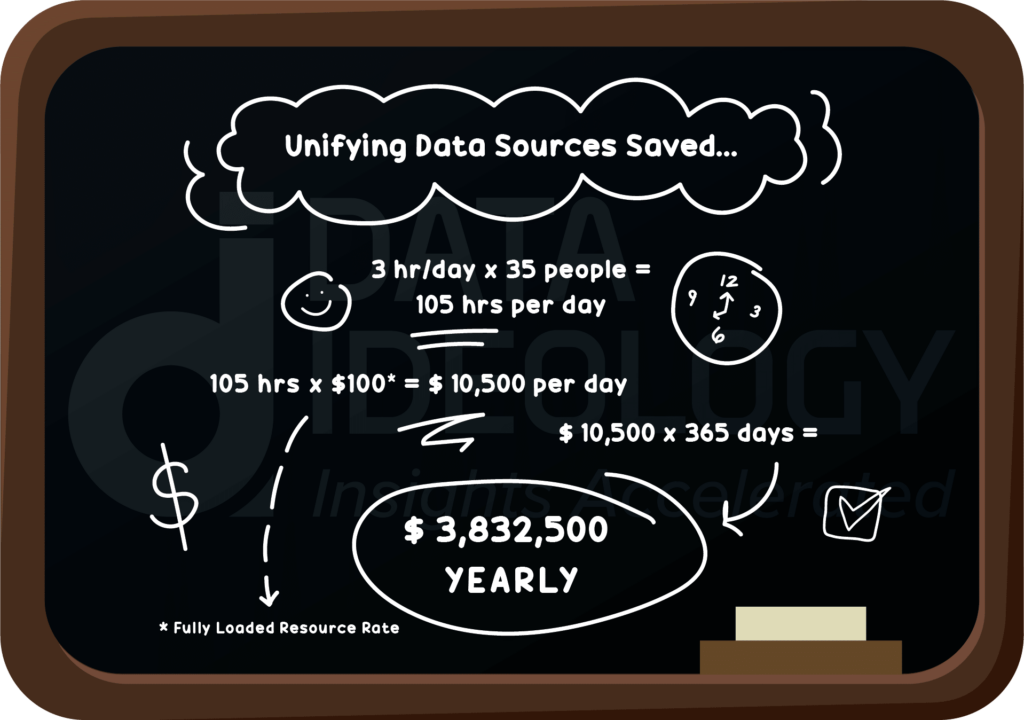
By centralizing all data sources and aligning that framework with business goals, the organization began breaking down data silos and optimized their data with a consolidated approach that saved the organization nearly $4 MM yearly in operational efficiencies. Within this centralized approach, clinical personnel now have timely access to the full breadth of trusted data and can make informed decisions about best care practices that relate directly to the member’s health.
To take this a step further, harnessing a single source of quality data allowed for continuous tracking and monitoring of quality metrics over time, making it possible for automation of patient follow-ups and outreach. Automation helped increase quality scores (HEDIS and Stars Ratings) and more importantly, improve the quality of care that members experience for the organization.
Start with a data strategy session.
See if you meet our criteria for a free consuling session.
Schedule with usFeatured Blog
Enterprise Data Strategy: What is it? And why is it important?
According to a recent study, organizations that utilize data management resources, such as an enterprise data strategy, are 58% more likely to surpass revenue goals...
READ MOREFeatured Case Study
Eliminating Data Silos saves Healthcare Payer nearly $4 MM yearly
Explore how Data Ideology helped a healthcare organization eliminate data silos and save $4 MM yearly with an updated system.
READ MORE